Steps to Setup Lambda to Start / Stop EC2 instances:
1) Create a Lambda Function with 'Author from scratch' and with Function name 'ecStartInstance' and Runtime 'Python 3.8'
2) Choose new role with basic Lambda permission
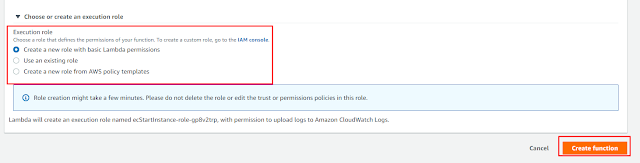
3) Create policy using IAM role
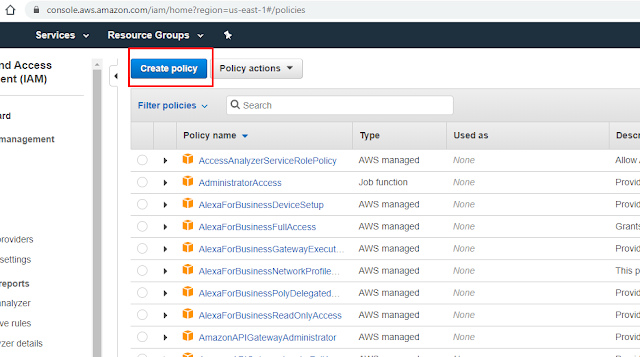
4) Click on JSON Editor option and update EC2 instance policy json and click on 'Review Policy'
JSON:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "logs:CreateLogGroup", "logs:CreateLogStream", "logs:PutLogEvents" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*" }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:Start*", "ec2:Stop*" ], "Resource": "*" } ] }
5) Give name and description for the policy and click on 'Create Policy'.
6) Edit the IAM role & add IAM Policy to that.
Click on IAM role. Click on 'Attach Policies' and select 'ec_start_stop_lambda' .
7) Write Lambda Function and select 'Configure test event'.
code:
import boto3
region = 'us-east-1'
instances = ['i-0a43e8f5990e24627',]
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=region)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2.start_instances(InstanceIds=instances)
print('stopped your instances: ' + str(instances))
8) Give event name 'ecStartEvent'
9) Edit basic settings, set timeout as 10 seconds.
10) To test the lambda function, click on 'Test' button.
Thats it.










Comments
Post a Comment