Step 1:
Move to Cloud Watcher console of aws.
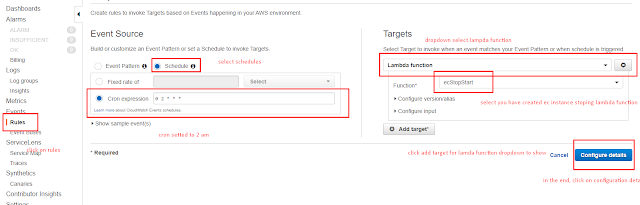
1) Click on Rules Menu.
2) Click on Schedule option once moved to rules menu
3) Give Crontab schedule expression, In my case, Instance should be stopped by 2AM everyday.
4) Click on 'Add Target' in the right side.
4a) Once dropdown appears, select Lambda Function.
4b) Function dropdown, select your lambda function, i.e. ecStopStart
5) Finally click on, configure details.
6) Cron Expression hours and day will work upon the timezone. It is with GMT. I have updated it to +5hrs 30mins UTC.
7) In the configuration details page, provide name, description and enable the the configuration.
8) Thats it.
Source : aws-console ec2 instance stop & start with cloud watch



Comments
Post a Comment